Download the report
Harnessing RD&D effectively will enhance the feasibility, efficiency, and pace of Australia's energy transition.

Australia’s energy transition is at a pivotal moment. Strategic investment to maximise the impact of RD&D will be essential for Australia’s energy transition. CSIRO has identified RD&D opportunities to accelerate the development of low emissions technologies tailored to Australian needs.
RD&D will be pivotal in informing and driving the change required to achieve the energy transition and Australia’s net zero ambitions. It provides evidence and new knowledge to inform policy and industry decisions; it helps develop and demonstrate technologies to increase energy system security and resilience; it supports international collaboration to reduce duplication; and it creates new intellectual property that can position Australia to attract global investments in low emissions technologies and manufacturing.
This resource is designed to support constructive dialogue, leveraging national RD&D strengths and evolving with input from the research community and the progress of the energy transition.
RD&D opportunities across five major sectors
The State of Energy Transition Technologies study explores RD&D opportunities to support the adoption of technologies that can accelerate cost-effective, low-risk, and integrated technology pathways across five major sectors:
- Electricity
- Low Carbon Fuels
- Transport
- Industry
- Carbon Management
Within these, 14 subsectors and 43 technologies are analysed, each mapped to 18 Australian use cases. The study identifies enabling technologies, and high-impact RD&D opportunities that can accelerate deployment and achieve costs, performance and safety outcomes.
Key findings
Five cross-cutting RD&D themes have emerged that could help optimise efforts and enhance the feasibility, efficiency, and pace of Australia's energy transition.
- Tailoring solutions for Australia: Australia has unique challenges and opportunities for low emissions technologies associated with its geography, geology, industrial mix and energy systems that international stakeholders may not prioritise but are vital for Australia to address.
- Achieving and exceeding cost forecasts through RD&D: RD&D has a key role to play in achieving and exceeding 2050 levelised cost forecasts across both energy supply and demand technologies, through its potential to reduce input costs for demand-side technologies and improve technology capital and operating costs.
- Supporting the demonstration and scale-up of technologies: Of the 43 explored technologies, only 14 are currently regarded as ready for commercial deployment, highlighting the need for RD&D investment to both support demonstration and scale-up of technologies, and to achieve the benefits of learning by doing.
- Developing technology-agnostic energy efficiency solutions: RD&D to enhance the energy and fuel efficiency of demand-side technologies can improve the costs and performance of both incumbent technologies and their low emissions alternatives, which will be important for reducing emissions in both the short and long term.
- Enabling adoption through interdisciplinary research: Technical development is only one part of the puzzle and coordinated social, environmental, policy and regulation research actions will be important to address the drivers of and barriers to the uptake of these technologies.
With limited RD&D resources and many emerging low emissions technologies, Australia must strategically prioritise efforts through strong collaboration across research, government, and industry to maximise national benefit.
Our analysis is a toolkit for stakeholders looking to understand the broader technology systems, the role of RD&D, and the key cost drivers of low emissions technologies for each subsector.
Read the full report
- The State of Energy Transition Technologies - synthesis report
- The State of Energy Transition Technologies - synthesis report (accessible text)
Future insights from levelised cost analysis
The cost analysis in the report is a key tool for guiding energy investment and decision-making. The National Energy Analysis Centre (NEAC) is working to digitise the State of Energy Transition Technologies levelised cost analysis, allowing users to test assumptions, explore sensitivities, consider more use cases, and download outputs. Feedback is invited on which features and insights would make this tool most valuable via this short NEAC survey.
Download the report
- The State of Energy Transition Technologies - synthesis report PDF (3 MB)
- Technical Appendix: Electricity PDF (3 MB)
- Technical Appendix: Low Carbon Fuels PDF (5 MB)
- Technical Appendix: Industry PDF (4 MB)
- Technical Appendix: Transport PDF (5 MB)
- Technical Appendix: Carbon Management PDF (3 MB)
- Technical Appendix: Levelised Cost Analysis PDF (2 MB)
Harnessing RD&D effectively will enhance the feasibility, efficiency, and pace of Australia's energy transition.
Front cover of the State of the Energy Transition Technologies Report. Synthesis Report.
Australia’s energy transition is at a pivotal moment. Strategic investment to maximise the impact of RD&D will be essential for Australia’s energy transition. CSIRO has identified RD&D opportunities to accelerate the development of low emissions technologies tailored to Australian needs.
RD&D will be pivotal in informing and driving the change required to achieve the energy transition and Australia’s net zero ambitions. It provides evidence and new knowledge to inform policy and industry decisions; it helps develop and demonstrate technologies to increase energy system security and resilience; it supports international collaboration to reduce duplication; and it creates new intellectual property that can position Australia to attract global investments in low emissions technologies and manufacturing.
This resource is designed to support constructive dialogue, leveraging national RD&D strengths and evolving with input from the research community and the progress of the energy transition.
RD&D opportunities across five major sectors
The State of Energy Transition Technologies study explores RD&D opportunities to support the adoption of technologies that can accelerate cost-effective, low-risk, and integrated technology pathways across five major sectors:
- Electricity
- Low Carbon Fuels
- Transport
- Industry
- Carbon Management
Within these, 14 subsectors and 43 technologies are analysed, each mapped to 18 Australian use cases. The study identifies enabling technologies, and high-impact RD&D opportunities that can accelerate deployment and achieve costs, performance and safety outcomes.
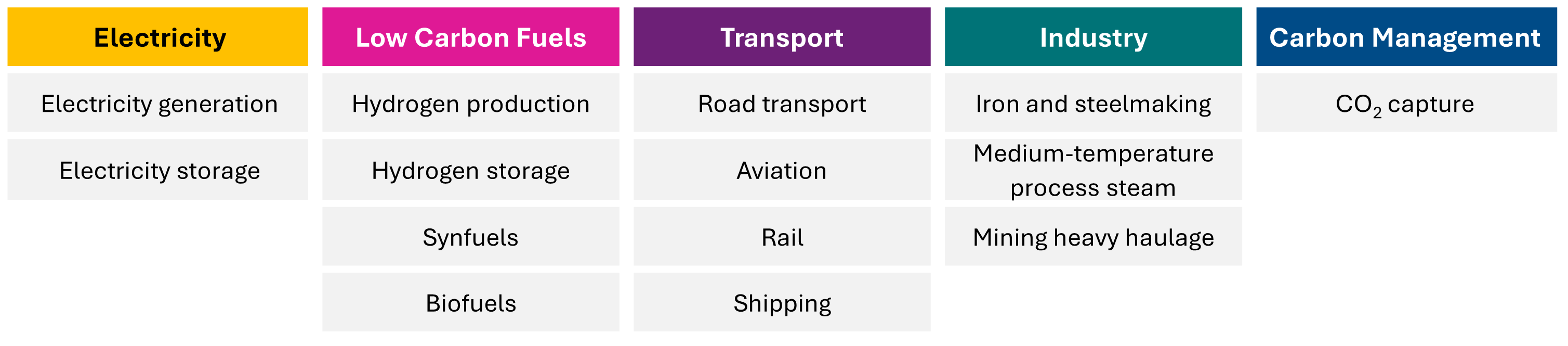
The table shows the five major sectors (Electricity, Low Carbon Fuels, Transport, Industry and Carbon Management) that the The State of the Energy Transition Technologies Report explored to support the adoption of technologies that can accelerate cost-effective, low-risk, and integrated technology pathways. It also shows 14 subsectors within those five major sectors, which include: Electricity Generation, Electricity Storage, Hydrogen Production, Hydrogen Storage, Synfuels, Biofuels, Road Transport, Aviation, Rail, Shipping, Iron and Steelmaking, Medium Temperature process Steam, Mining heavy Haulage and CO2 Capture.
Electricity (yellow header)
Low Carbon Fuels (pink header)
Transport (purple header)
Industry (teal header)
Carbon Management (blue header)
Electricity generation
Hydrogen production
Road transport
Iron and steelmaking
CO₂ capture
Electricity storage
Hydrogen storage
Aviation
Medium-temperature process steam
Synfuels
Rail
Mining heavy haulage
Biofuels
Shipping
Key findings
Five cross-cutting RD&D themes have emerged that could help optimise efforts and enhance the feasibility, efficiency, and pace of Australia's energy transition.
- Tailoring solutions for Australia: Australia has unique challenges and opportunities for low emissions technologies associated with its geography, geology, industrial mix and energy systems that international stakeholders may not prioritise but are vital for Australia to address.
- Achieving and exceeding cost forecasts through RD&D: RD&D has a key role to play in achieving and exceeding 2050 levelised cost forecasts across both energy supply and demand technologies, through its potential to reduce input costs for demand-side technologies and improve technology capital and operating costs.
- Supporting the demonstration and scale-up of technologies: Of the 43 explored technologies, only 14 are currently regarded as ready for commercial deployment, highlighting the need for RD&D investment to both support demonstration and scale-up of technologies, and to achieve the benefits of learning by doing.
- Developing technology-agnostic energy efficiency solutions: RD&D to enhance the energy and fuel efficiency of demand-side technologies can improve the costs and performance of both incumbent technologies and their low emissions alternatives, which will be important for reducing emissions in both the short and long term.
- Enabling adoption through interdisciplinary research: Technical development is only one part of the puzzle and coordinated social, environmental, policy and regulation research actions will be important to address the drivers of and barriers to the uptake of these technologies.
With limited RD&D resources and many emerging low emissions technologies, Australia must strategically prioritise efforts through strong collaboration across research, government, and industry to maximise national benefit.
Our analysis is a toolkit for stakeholders looking to understand the broader technology systems, the role of RD&D, and the key cost drivers of low emissions technologies for each subsector.
Read the full report
- The State of Energy Transition Technologies - synthesis report PDF (3 MB)
- The State of Energy Transition Technologies - synthesis report (accessible text) TXT (88 KB)
Future insights from levelised cost analysis
The cost analysis in the report is a key tool for guiding energy investment and decision-making. The National Energy Analysis Centre (NEAC) is working to digitise the State of Energy Transition Technologies levelised cost analysis, allowing users to test assumptions, explore sensitivities, consider more use cases, and download outputs. Feedback is invited on which features and insights would make this tool most valuable via this short NEAC survey.
